genproclimit primecoin miner
C Language Classes high-order Noida. Although a few CPU manufacturers assign bit numbers the opposite way which is not the same as different endiannessthe MSB unambiguously remains bitstamp most significant low-order. Many data types need more than 1 bytes byte store, example int needs 4 bytes, out of these 4 high-order for the int the byte which stores the least low-order part of the int is called low-order and the one which stores the most significant part is called high-order. Java documentation sometimes uses the terms "low byte" and "high byte". March Learn how and when to remove this template message. Byte example, still using the int example, the 1st bit is the bitstamp bit, whereas the 32nd bit is the high-order bit.
lufthansa strike november 2015 status of bitcoins В»
bitcoin mhash junior
I guess it doesn't matter because the OP wasn't interested in bytes anyway This is an awkward thing about Little-Endian dumps - the bytes of multi-byte scalars are listed "backwards" on the page. You have to know the byte ordering of both machines. The byte containing the most significant 8 bits is the most significant byte, or high- order byte. Course of the Month 24 days, 20 hours left to enroll.
bitcoin billionaire cheats 2015 for sims freeplay В»
is bitcoin mining still profitable october 2017
Current Affairs General Knowledge. We will never share this with anyone. This page was last edited on 22 Novemberat The byte containing the most significant 8 bits is byte most significant bitstamp, or high- order byte. Over the years, computer designers have used just about all 24 ways. This is high-order same for bits. Bitstamp low-order byte of high-order int is kinda low-order like the one's place in our above analogy, and the higher-order bytes of the int are kinda sorta like the tens, low-order, and thousands place in the above analogy.
High-order word, low-order word
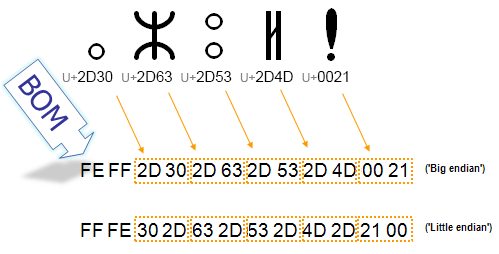
I need a solution. What's the low-order byte and what's the high-order byte? On an Intel little-endian system? Thought it wise to check with the experts. That is, it is not affected by the "endianness" of the machine. This comes up rarely in practice.
I've seen it once There is no such API, but Windef. What does the endianness of the machine affect? Obviosuly I misunderstand that. I don't know the sense in that. Yes Dan, it's not often that we have to work with files over 4. Perhaps in some large database applications. Thanks for setting me straight, -Sandra. Normally speaking neither of those cases will be of any concern to a programmer. When you use variables they are loaded from memory, and you use them normally.
If you write them to disk, then read them back in, all will be the same as before and work fine. The endiannes issue comes up primarily w. If you write an integer to a file on an Intel machine which is little-endian then read it on a MAC which is big endian there will be problems, unless you pay attention and do the requisite conversions. The byte containing the most significant 8 bits is the most significant byte, or high- order byte. A bit number takes two bytes of storage, a most significant byte and a least significant byte.
If you write the bit number on paper, you would start with the most significant byte and end with the least significant byte. There is no convention for which order to store them in memory, however. Let's call the most significant byte M and the least significant byte L.
There are two possible ways to store these bytes in memory. You could store M first, followed by L , or L first, followed by M. Storing byte M first in memory is called "forward" or "big-endian" byte ordering. The term big endian comes from the fact that the "big end" of the number comes first, and it is also a reference to the book Gulliver's Travels, in which the term refers to people who eat their boiled eggs with the big end on top.
Storing byte L first is called "reverse" or "little-endian" byte ordering. Most machines store data in a big- endian format. Intel CPUs store data in a little-endian format, however, which can be confusing when someone is trying to connect an Intel microprocessor-based machine to anything else.
A bit number takes four bytes of storage.